produktkategori
Produkttaggar
3 axel, 5 axel CNC-fräsning precisionsbearbetning
CNC-fräsmaskinen kan bearbeta komplexa former av roterande kroppar. I fräsning, ämnet fixeras först, och en höghastighets roterande fräs används för att flytta ämnet på ämnet för att fräsa ut den önskade formen och egenskaperna. Traditionell fräsning används mest för att fräsa enkla formegenskaper som konturer och spår. CNC-fräsmaskinen kan bearbeta komplexa former och funktioner. Fräsnings- och borrbearbetningscentret kan utföra treaxlig eller fleraxlig fräsning och borrning för bearbetning: formar, inspektionsverktyg, formar, tunnväggiga komplexa krökta ytor, konstgjorda proteser, pumphjulsblad, etc. Vid val av CNC-fräsdelar, fördelarna och nyckelfunktionerna hos CNC-fräsmaskiner bör utnyttjas fullt ut.
CNC milling is a high-tech processing method for precision parts, which can be processed into parts with complex structures combined with square and circular shapes.
CNC-fräsmaskinen kan bearbeta komplexa former av roterande kroppar. I fräsning, ämnet fixeras först, och en höghastighets roterande fräs används för att flytta ämnet på ämnet för att fräsa ut den önskade formen och egenskaperna. Traditionell fräsning används mest för att fräsa enkla formegenskaper som konturer och spår. CNC-fräsmaskinen kan bearbeta komplexa former och funktioner. Fräsnings- och borrbearbetningscentret kan utföra treaxlig eller fleraxlig fräsning och borrning för bearbetning: formar, inspektionsverktyg, formar, tunnväggiga komplexa krökta ytor, konstgjorda proteser, pumphjulsblad, etc. Vid val av CNC-fräsdelar, fördelarna och nyckelfunktionerna hos CNC-fräsmaskiner bör utnyttjas fullt ut.
Olika typer av material kan bearbetas, Till exempel 316, 304 rostfritt stål, kolstål, legerat stål, legerat aluminium, Zink Alloy, titanlegering, koppar, järn, akryl, Teflon, POM rods and other metal and plastic raw materials.
The difference between turning and milling
Turning and milling is a common metal cold working method. The difference from turning is that in milling, the tool rotates at a high speed under the drive of the spindle, while the workpiece is relatively stationary.
The difference between turning and milling:
Turning is used to machine rotating parts. The parts are clamped on the main shaft of the machine tool through the three gripping chucks and rotate at high speed. Then use a turning tool to move the tool according to the generatrix of the revolving body to cut out the shape of the product. The lathe can also process the inner hole, tråd, biting, etc. The latter two are low-speed processing.
Milling process
(1) Milling the curve contour on the workpiece, straight line, arc, thread or spiral curve, especially the non-circular curve and list curve given by mathematical expression.
(2) Milling the spatial curve or surface of the given mathematical model.
(3) Although the milling shape is simple, the product has a wide range of sizes and positions where internal inspection is difficult.
(4) The milling machine can process cavities, box parts, etc. that are difficult to observe, control and detect when processed by ordinary machine tools.
(5) Holes or planes with strict size requirements.
(6) All simple surfaces or shapes can be processed by milling in one clamping.
(7) General processing that can effectively improve productivity and reduce labor intensity by using CNC milling processing.
The main processing objects suitable for CNC milling include the following categories: plane contour parts, variable bevel parts, spatial curved surface contour parts, holes and threads, etc.
Operation points of milling
- The milling machine operator should wear tight-fitting work clothes with cuffs tied tightly; Female operators must wear protective caps; Wear protective glasses when high-speed milling; Wear a mask when milling iron castings; It is strictly forbidden to wear gloves during operation to prevent your hands from being caught between the rotating tool and the workpiece.
2. Before operation, check whether the parts and safety devices of the milling machine are safe and reliable;
Check whether the electrical parts of the equipment are safe and reliable.
3. When loading and unloading workpieces, the workbench should be returned to a safe position. When using a wrench to tighten the workpiece, the direction of force should avoid the milling cutter to prevent the wrench from hitting the tool or fixture when it slips.
4. When assembling and disassembling the milling cutter, use a special pad to pad it. Do not hold the milling cutter directly with your hands.
5. When milling irregular workpieces and using vise, dividing head and special fixture to hold the workpiece. The center of gravity of irregular workpieces, vices, indexing heads, special fixtures, etc. should be placed in the middle of the workbench as much as possible to avoid uneven force and deformation of the workbench.
6. During fast or automatic feed milling, do not move the worktable to the two extremes to avoid squeezing the screw rod.
7. When the milling machine is running, it is not allowed to adjust, measure the workpiece and change the lubrication method to prevent the hand from touching the tool and hurting the fingers.
8. Before the rotation of the milling cutter is completely stopped, it is not allowed to brake by hand.
9. Do not remove the chips by hand or blow with your mouth during milling to prevent the chips from damaging the skin and eyes.
10. During motorized rapid feed, the handle wheel clutch should be opened to prevent the hand wheel from rotating quickly and hurting people.
11. When the workbench is reversing, the reversing handle must be stopped at the middle position first, and then reversing. Direct reversal is not allowed.
12. When milling keyway shafts or milling thin workpieces, prevent the surface of the indexing head or worktable from being milled.
13. When milling a plane, a cutter head with more than four milling cutter heads must be used, and an appropriate cutting amount must be selected to prevent the machine tool from vibration during milling.
14. After work, stop the workbench at the middle position, and drop the lifting platform to the lowest position.
15. For CNC vertical milling machines, pre-select items such as work procedures, spindle speed, tool feed, tool motion trajectory, and continuous offsides according to technological requirements before work. Put the electric knob in the "adjustment" position for trial run. After confirming that there is no problem, put the electric knob in the automatic or semi-automatic position to work.

5 axel Fräsning av aluminium Kavitet
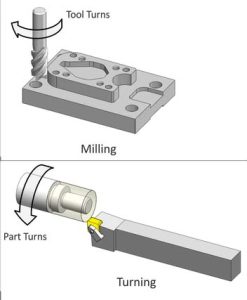
difference between turning and milling
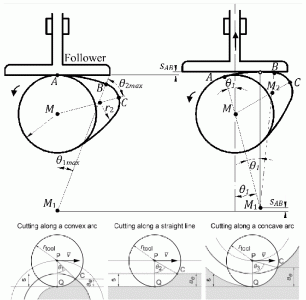
Milling process of curve contour, straight line and arc
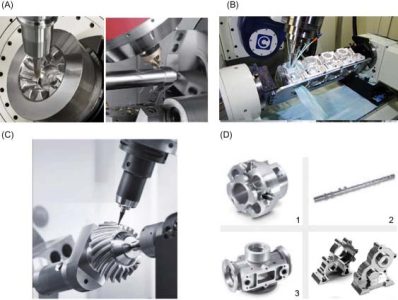
5-axis milling housing curved contour
Kontakta oss
Väntar på ditt mejl, vi kommer att svara dig inom 12 timmar med värdefull information du behövde.
 English
English العربية
العربية 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Slovenčina
Slovenčina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Türkçe
Türkçe




