Kategórie produktov
Štítky produktu
prispôsobená veľká CNC obrábacia časť
Technická problematika CNC obrábania spracovávaných dielov zahŕňa široké spektrum aspektov. Nasleduje kombinácia možnosti a pohodlia programovania na predloženie nejakého hlavného obsahu, ktorý je potrebné analyzovať a preskúmať.
Process analysis of CNC machining parts
Technická problematika CNC obrábania spracovávaných dielov zahŕňa široké spektrum aspektov. Nasleduje kombinácia možnosti a pohodlia programovania na predloženie nejakého hlavného obsahu, ktorý je potrebné analyzovať a preskúmať.
1. Dimenzovanie by malo zodpovedať charakteristikám CNC obrábania
V CNC programovaní, veľkosť a polohu všetkých bodov, linky, a povrchy sú založené na pôvode programovania. Preto, najlepšie je zadať veľkosť súradníc priamo na výkrese dielu, alebo skúste uviesť veľkosť s rovnakým dátumom.
2. Podmienky geometrických prvkov by mali byť úplné a presné
V programovaní, programátori musia plne pochopiť parametre geometrických prvkov tvoriacich obrys dielu a vzťah medzi geometrickými prvkami. Pretože všetky geometrické prvky obrysu dielu musia byť definované pri automatickom programovaní. Pri manuálnom programovaní, musia sa vypočítať súradnice každého uzla. Bez ohľadu na to, ktorý bod je nejasný alebo neistý, programovanie nie je možné vykonať.
Avšak, v dôsledku nedostatočného zohľadnenia alebo zanedbania zo strany dizajnérov dielov v procese navrhovania, často sa vyskytujú neúplné alebo nejasné parametre, ako napr: oblúk a priamka, oblúk a oblúk sú dotyčnice alebo sa pretínajú alebo oddelené.
Preto, pri prezeraní a analýze výkresov, musíte byť opatrní a v prípade zistenia problémov včas kontaktovať projektanta.
3. Spoľahlivá referenčná poloha
V CNC obrábaní, procesy obrábania sú často koncentrované, a je veľmi dôležité nájsť na rovnakej referencii. Preto, často je potrebné nastaviť nejaké pomocné vzťažné body alebo pridať nejaké procesné náliatky na polotovar.
4. Jednotný typ alebo veľkosť geometrie
Najlepšie je prijať jednotný geometrický typ alebo veľkosť pre tvar a dutinu dielov. To môže znížiť počet výmen nástrojov, a taktiež je možné použiť ovládacie programy alebo špeciálne programy na skrátenie dĺžky programu. Tvar dielov je čo najviac symetrický, čo je vhodné na programovanie pomocou funkcie zrkadlového obrábania CNC obrábacieho stroja, aby sa ušetril čas programovania.
Upínanie obrábaných dielov
- Základné princípy umiestnenia a inštalácie
Pri obrábaní dielov na CNC obrábacom stroji, Základným princípom polohovania a inštalácie je výber primeraného polohovacieho základu a plánu upnutia. Pri výbere venujte pozornosť nasledujúcim bodom:
1. Snažte sa o zjednotenie dizajnu, procesné a programovacie výpočtové benchmarky.
2. Minimalizujte počet upínacích časov, a po umiestnení a upnutí raz spracujte všetky povrchy, ktoré sa majú spracovať.
3. Avoid the use of machine-occupied manual-adjustable processing schemes to give full play to the effectiveness of CNC machine tools.Ii. Basic principles for selecting fixtures
The characteristics of CNC machining put forward two basic requirements for the fixture:
One is to ensure that the coordinate direction of the fixture is relatively fixed with the coordinate direction of the machine tool;
The second is to coordinate the size relationship between the parts and the machine coordinate system. Navyše, the following points should be considered:
1. When the batch of parts is not large, modular fixtures, adjustable fixtures and other general fixtures should be used as much as possible to shorten production preparation time and save production costs.
2. Only consider the use of special fixtures during mass production, and strive for a simple structure.
3. The loading and unloading of parts should be fast, convenient and reliable to shorten the machine stop time.
4. The parts on the fixture should not hinder the machining of the surfaces of the parts by the machine tool, to jest, the fixture should be open. Its positioning and clamping mechanism components cannot affect the tool in the machining process (such as collisions, atď.).
Program structure
A program segment is a continuous group of words that can be processed as a unit, and it is actually a section of a program in a CNC machining program. The main body of the part processing program is composed of several program segments. Most program segments are used to instruct the machine tool to complete or execute a certain action.
The block is composed of size characters, non-size characters and block end instructions. When writing and printing, each block generally occupies one line, and the same is true when the program is displayed on the screen.Program format
The conventional processing program is composed of start character (single row), program name (single row), program body and program end instruction (generally single row). There is a program end character at the end of the program.
The program start character and the program end character are the same character:
It is% in ISO code and ER in EIA code. The program end instruction can be M02 (program end) or M30 (paper tape end).
CNC machine tools generally use stored programs to run. V tomto čase, spoločné body M02 a M30 sú:
Po dokončení všetkých ostatných príkazov v aktuálnom bloku, slúži na zastavenie vretena, chladiaca kvapalina a krmivo, a resetujte riadiaci systém.
M02 a M30 sú úplne ekvivalentné pri použití na niektorých obrábacích strojoch (systémov), pričom na iných obrábacích strojoch sa používajú nasledujúce rozdiely (systémov): Keď je program ukončený s M02, kurzor sa zastaví na konci programu po skončení automatickej prevádzky; Keď program ukončí M3O, kurzor a zobrazenie na obrazovke sa po skončení automatickej prevádzky môže automaticky vrátiť na začiatok programu, a program je možné znova spustiť stlačením tlačidla štart. Hoci M02 a M30 môžu zdieľať blok s inými programovými slovami, it is better to list them in a single block or share a block with the sequence number only.The program name is located before the main body of the program and after the start of the program, and it usually occupies a line on its own. The program name has two forms:
One is composed of prescribed English characters (usually O), followed by several digits. The maximum allowable number of digits is stipulated by the manual, and the two common ones are two digits and four digits. This form of program name can also be called a program number. Another form is that the program name is composed of English characters, numbers or a mixture of English and numbers, and a “-” sign can be added in the middle. This form makes the user naming procedure more flexible. Napríklad, the program for the third process of machining the flange with the part drawing number 215 on the LC30 CNC lathe can be named LC30-FIANGE-215-3. This brings great convenience to use, storage and retrieval. The format of the program name is determined by the CNC system.
%
O1001
N0 G92 X0 Y0 Z0
N5 G91 G00 X50 Y35 S500 MO3
N10 G43 Z-25 T01.01
N15 G01 G007 Z-12
N20 G00 Z12
N25 X40
N30 G01 Z-17
N35 G00 G44 Z42 M05
N40 G90 X0 Y0
N45 M30
%Programming section format
The rules for the arrangement of words, characters and data in a program segment are called block format. The fixed sequence format and separator (HT or TAB) block format have been used in CNC history. When these two program segment formats have passed, the word address variable program segment format is widely used at home and abroad, známy aj ako formát adresy slova.
V tomto formáte, dĺžka programového slova nie je pevná, a počet slov programu je tiež variabilný. Väčšina CNC systémov umožňuje ľubovoľné usporiadanie postupnosti programových slov, takže patria do formátu variabilného bloku. Avšak, väčšinou, pre pohodlie pri písaní, zadávanie, kontrola a korektúry, programové slová sú v segmente programu usporiadané v určitom poradí.
Programovacie pokyny CNC obrábacích strojov používajú podrobné formáty na klasifikáciu a špecifikáciu detailov programovania: Znaky používané pri programovaní, poradie a dĺžka slova programových slov v segmente programu, atď. napr:/ NO3 G02 X+053 Y+053 I0 J+053 F031 S04 T04 M03 LF
Podrobný popis klasifikácie formátu vo vyššie uvedenom príklade je nasledujúci: N03 is the sequence number of the program segment; G02 means that the processing track is a clockwise arc; X+053, Y+053 indicate the coordinates of the end point of the arc to be processed; I0, J+053 represent the center coordinates of the arc to be processed; F031 is the processing feed rate; S04 is the spindle speed; T04 is the tool number of the tool used; M03 is an auxiliary function command; LF block end instruction; /Select instructions for skipping. The function of skip selection instruction is: On the premise that the program remains unchanged, the operator can choose whether to execute or not to execute the blocks in the program with skip selection instructions. The method of selection is usually by turning the step selection switch on the operation panel to ON or OFF to realize that the program segment with “/” is not executed or executed.

milwaukee wisconsin machining services

presné zostavy Upínanie obrábaných dielov

Programming of CNC machining steel parts

CNC machining parts different program structure
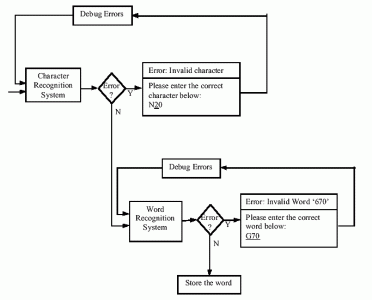
CNC machining components Program execution process
Execution of the program
This is sometimes encountered in the preparation of processing programs: A group of blocks appears multiple times in a program, or it is used in several programs. We can extract this group of program segments, name them and store them separately. This group of program segments is a subroutine. A subroutine is a section of processing program that can be called by appropriate machine control instructions, and it generally has an independent meaning in processing. The processing program where the instruction to call the subroutine of the first level is located is called the main program. The instruction of the subroutine is also a program segment, which is generally composed of the subroutine call instruction, the subroutine name, and the number of calls. The specific rules and formats vary from system to system. Napríklad, it is also "call subroutine No. 55 once", FANUC system uses "M98 P55.", and American A-B company system uses "P55x".
Subroutines can be nested, to jest, layer by layer. The relationship between the upper level and the next level is the same as the relationship between the main program and the first level subroutine. The maximum number of layers that can be set depends on the specific CNC system. The form and composition of the subroutine are roughly the same as the main program: The first line is the subroutine number (name), the last line is the "subroutine end" instruction, and the main body of the subroutine is between them. Avšak, the function of the main program end instruction is to end the main program and reset the CNC system. The instructions have been standardized, and each system uses M02 or M30; The function of the subroutine end instruction is to end the subroutine, return to the main program or the upper level subroutine. The commands are not unified in various systems, such as M99 for FANUC system, M17 for Siemens system, and M02 for system of American A-B company.
User macros (programs) can be used in CNC machining programs. The so-called macro program is a subroutine containing variables. Inštrukcia, ktorá v programe volá program makra, sa nazýva inštrukcia používateľského makra, a funkcia, ktorú systém môže použiť program užívateľského makra, sa nazýva funkcia užívateľského makra. Pri vykonávaní, stačí napísať príkaz užívateľského makra na vykonanie jeho funkcie užívateľského makra.
Najväčšie vlastnosti používateľských makier sú:
● V používateľských makrách možno použiť premenné;
●Môže používať výpočtové vzorce, otočné príkazy a rôzne funkcie
●Príkazy používateľského makra možno použiť na priradenie hodnôt premenným.
CNC obrábacie stroje využívajú na spracovanie dielov skupinovú technológiu, ktorý môže rozšíriť veľkosť dávky, obmedziť programovanie, a zlepšiť ekonomické výhody. V skupinovom spracovaní, diely sú klasifikované, a program spracovania je zostavený pre tento typ častí, namiesto úpravy programu pre každú časť. Pri spracovaní rovnakého typu dielov s rôznymi veľkosťami, hlavnou výhodou používania používateľských makier je, že namiesto konkrétnych hodnôt možno použiť premenné. Pokiaľ ide o skutočné spracovanie, je len potrebné priradiť hodnotu skutočnej veľkosti tejto časti premennej pomocou príkazu užívateľského makra.
Kontaktuj nás
Čaká sa na váš e-mail, odpovieme vám v rámci 12 hodiny s cennými informáciami, ktoré ste potrebovali.
 English
English العربية
العربية 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Slovenčina
Slovenčina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Türkçe
Türkçe





