Productcategorieën
Productlabels
Opspanning en gereedschapsinstelling van draaibankonderdelen
Opspannen van draaigereedschappen
1) De schacht van het draaigereedschap mag niet te lang uit de gereedschapshouder steken, en de algemene lengte mag niet groter zijn dan 1.5 maal de hoogte van de gereedschapsschacht (behalve het draaien van gaten, groeven, enz.)
2) De middellijn van de gereedschapsbalk van het draaigereedschap moet loodrecht of evenwijdig aan de snijrichting staan.
3) Aanpassing van de hoogte van de gereedschapspunt:
General technical code for turning metal processing (JB/T9168.2-1998)
Opspannen van draaigereedschappen
1) De schacht van het draaigereedschap mag niet te lang uit de gereedschapshouder steken, en de algemene lengte mag niet groter zijn dan 1.5 maal de hoogte van de gereedschapsschacht (behalve het draaien van gaten, groeven, enz.)
2) De middellijn van de gereedschapsbalk van het draaigereedschap moet loodrecht of evenwijdig aan de snijrichting staan.
3) Aanpassing van de hoogte van de gereedschapspunt:
(1) When turning the end face, turning taper surface, draaiende draad, turning forming surface and cutting solid workpieces, the tool tip should generally be the same height as the axis of the workpiece.
(2) Rough turning of the outer circle, fine turning of the hole, and the tool tip should generally be slightly higher than the axis of the workpiece.
(3) When turning slender shaft pins, rough turning holes, and cutting hollow workpieces, the tool tip should generally be slightly lower than the axis of the workpiece.
4) The bisector of the nose angle of the thread turning tool should be perpendicular to the axis of the workpiece.
5) When clamping the turning tool, the shims under the tool bar should be small and flat, and the screws for pressing the turning tool should be tightened.
Clamping of turning hardware parts
1) When using a three-jaw self-centering chuck to clamp a workpiece for rough turning or finishing turning, if the diameter of the workpiece is less than 30 mm, the overhang length of the workpiece should not be greater than 5 times the diameter. If the diameter of the workpiece is greater than 30 mm, the overhang length of the workpiece should not be greater than 3 times the diameter.
2) When using four-jaw single-action chuck, faceplate, angle iron (bent plate), enz. to clamp irregular and heavy workpieces, a counterweight must be added.
3) When machining shaft pin workpieces between thimble fixtures, adjust the tailstock center axis to coincide with the lathe spindle axis before turning.
4) When machining a slender shaft between two thimble fixtures, the tool holder or center holder should be used. Pay attention to adjusting the top tightening force during processing, and the dead center and center frame should be lubricated.
5) When using the tailstock, extend the sleeve as short as possible to reduce vibration.
6) When clamping a workpiece with a small supporting surface and high height on a vertical car, use a raised jaw and add a tie rod or a pressure plate to the appropriate position to compress the workpiece.
7) When turning wheel and sleeve castings and forgings, they should be aligned according to the unprocessed surface to ensure uniform wall thickness after processing.
Turning process of hardware parts
1) When turning the stepped shaft of the turning table, in order to ensure the rigidity during turning, generally the position with the larger diameter should be turned first, and the position with the smaller diameter should be turned later.
2) When grooving the workpiece on the shaft, it should be performed before finishing to prevent deformation of the workpiece.
3) When finishing turning a threaded shaft, generally you should finish turning the unthreaded position after threading.
4) Before drilling, the end face of the workpiece should be turned flat. Indien nodig, drill the center hole first.
5) When drilling deep holes, generally drill pilot holes first.
6) When turning (Φ10—Φ20) ㎜ holes, the diameter of the tool bar should be 0.6—0.7 times the processed hole diameter;
When machining holes with a diameter greater than Φ20mm, generally the tool holder with the turning head should be used.
7) When turning multiple threads or multiple worms, try cutting after adjusting the gears.
8) When using an automatic lathe, adjust the relative position of the tool and the workpiece according to the adjustment card of the machine tool. After the adjustment is completed, test turning is required, and the first part can be processed only after it is qualified;
Pay attention to tool wear and workpiece size and surface roughness at any time during processing.
9) When turning on a vertical lathe, after the tool post is adjusted, the beam cannot be moved at will.
10) When the relevant surface of the workpiece has position tolerance requirements, try to complete the turning in one clamping.
11) When turning the cylindrical gear blank, the hole and the reference end face must be processed in one clamping. Indien nodig, a marking line should be drawn near the gear index circle on the end face.
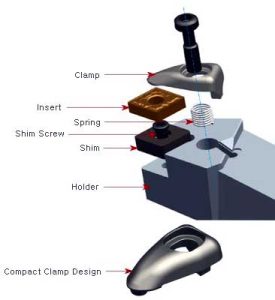
Clamping method of turning tool

Zelfcentrerende klauwplaat met drie klauwen voor het spannen en draaien van werkstukken
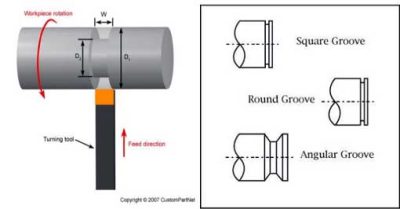
Ways of turning stepped shafts

Finish turning threaded shaft

Smooth turning of the end face of the workpiece
Neem contact met ons op
Wachten op uw e-mail, wij zullen u binnen antwoorden 12 uur met waardevolle informatie die u nodig had.
 English
English العربية
العربية 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Slovenčina
Slovenčina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Türkçe
Türkçe





