제품 카테고리
- CNC 밀링 서비스 31
- CNC 스탬핑 서비스 0
- CNC 판금 0
- 신속한 프로토 타입 12
- 스탬핑 다이 0
- 티타늄 합금 부품 4
- 스테인레스 스틸 부품 5
- 알루미늄 밀링 부품 14
- CNC 터닝 서비스 16
맞춤형 대형 CNC 가공 부품
가공된 부품의 CNC 가공에 관한 기술적 문제는 다양한 측면을 포함합니다.. 다음은 분석하고 검토해야 할 몇 가지 주요 내용을 제시하기 위해 프로그래밍의 가능성과 편의성을 결합한 것입니다..
Process analysis of CNC machining parts
가공된 부품의 CNC 가공에 관한 기술적 문제는 다양한 측면을 포함합니다.. 다음은 분석하고 검토해야 할 몇 가지 주요 내용을 제시하기 위해 프로그래밍의 가능성과 편의성을 결합한 것입니다..
1. The dimensioning should conform to the characteristics of CNC machining
In CNC programming, the size and position of all points, lines, and surfaces are based on the programming origin. 그러므로, it is best to give the coordinate size directly on the part drawing, or try to quote the size with the same datum.
2. The conditions of geometric elements should be complete and accurate
In programming, programmers must fully grasp the geometric element parameters constituting the contour of the part and the relationship between the geometric elements. Because all geometric elements of the contour of the part must be defined during automatic programming. When manually programming, the coordinates of each node must be calculated. No matter which point is unclear or uncertain, programming cannot be performed.
하지만, due to inadequate consideration or neglect by part designers in the design process, there are often incomplete or unclear parameters, ~와 같은: arc and straight line, arc and arc are tangent or intersected or separated.
그러므로, when reviewing and analyzing the drawings, you must be careful and contact the designer in time if you find any problems.
3. Reliable positioning reference
CNC 가공에서, the machining processes are often concentrated, and it is very important to locate on the same reference. 그러므로, it is often necessary to set some auxiliary datums or add some process bosses on the blank.
4. Unified geometry type or size
It is best to adopt a uniform geometric type or size for the shape and cavity of the parts. This can reduce the number of tool changes, and it is also possible to use control programs or special programs to shorten the program length. The shape of the parts is as symmetrical as possible, which is convenient for programming using the mirror machining function of the CNC machine tool to save programming time.
Clamping of machined parts
- Basic principles of positioning and installation
When machining parts on a CNC machine tool, the basic principle of positioning and installation is to select a reasonable positioning datum and clamping plan. Pay attention to the following points when choosing:
1. Strive to unify the design, process and programming calculation benchmarks.
2. Minimize the number of clamping times, and process all the surfaces to be processed after positioning and clamping once.
3. Avoid the use of machine-occupied manual-adjustable processing schemes to give full play to the effectiveness of CNC machine tools.II. Basic principles for selecting fixtures
The characteristics of CNC machining put forward two basic requirements for the fixture:
One is to ensure that the coordinate direction of the fixture is relatively fixed with the coordinate direction of the machine tool;
The second is to coordinate the size relationship between the parts and the machine coordinate system. 게다가, the following points should be considered:
1. When the batch of parts is not large, modular fixtures, adjustable fixtures and other general fixtures should be used as much as possible to shorten production preparation time and save production costs.
2. Only consider the use of special fixtures during mass production, and strive for a simple structure.
3. The loading and unloading of parts should be fast, convenient and reliable to shorten the machine stop time.
4. The parts on the fixture should not hinder the machining of the surfaces of the parts by the machine tool, 그건, the fixture should be open. Its positioning and clamping mechanism components cannot affect the tool in the machining process (such as collisions, 등.).
Program structure
A program segment is a continuous group of words that can be processed as a unit, and it is actually a section of a program in a CNC machining program. 부품 가공 프로그램의 본체는 여러 프로그램 세그먼트로 구성됩니다.. 대부분의 프로그램 세그먼트는 공작 기계에 특정 작업을 완료하거나 실행하도록 지시하는 데 사용됩니다..
블록은 크기 문자로 구성됩니다., 크기가 아닌 문자 및 블록 끝 명령어. 글을 쓰거나 인쇄할 때, 각 블록은 일반적으로 한 줄을 차지합니다., 프로그램이 화면에 표시될 때도 마찬가지입니다..프로그램 형식
기존 처리 프로그램은 시작 문자로 구성됩니다. (단일 행), 프로그램 이름 (단일 행), 프로그램 본체 및 프로그램 종료 명령 (일반적으로 단일 행). 프로그램 끝에 프로그램 종료 문자가 있습니다..
프로그램 시작 문자와 프로그램 종료 문자가 동일한 문자입니다.:
ISO 코드에서는 %이고 EIA 코드에서는 ER입니다.. 프로그램 종료 명령은 M02일 수 있습니다. (프로그램 종료) or M30 (paper tape end).
CNC machine tools generally use stored programs to run. 이때, the common points of M02 and M30 are:
After completing all other commands in the current block, it is used to stop the spindle, coolant and feed, and reset the control system.
M02 and M30 are completely equivalent when used on some machine tools (systems), while the following differences are used on other machine tools (systems): When the program is ended with M02, the cursor will stop at the end of the program after the automatic operation ends; When the program is terminated by M3O, the cursor and screen display can automatically return to the beginning of the program after the automatic operation is over, and the program can be run again by pressing the start button. Although M02 and M30 are allowed to share a block with other program words, it is better to list them in a single block or share a block with the sequence number only.The program name is located before the main body of the program and after the start of the program, and it usually occupies a line on its own. The program name has two forms:
One is composed of prescribed English characters (usually O), followed by several digits. The maximum allowable number of digits is stipulated by the manual, and the two common ones are two digits and four digits. This form of program name can also be called a program number. Another form is that the program name is composed of English characters, numbers or a mixture of English and numbers, and a “-” sign can be added in the middle. 이 양식을 사용하면 사용자 이름 지정 절차가 더욱 유연해집니다.. 예를 들어, 품명번호로 플랜지를 가공하는 3차 공정 프로그램 215 LC30 CNC 선반에서는 LC30-FIANGE-215-3으로 이름을 지정할 수 있습니다.. 이는 사용하기에 큰 편리함을 제공합니다, 저장 및 검색. 프로그램 이름의 형식은 CNC 시스템에 의해 결정됩니다..
%
O1001
N0 G92 X0 Y0 Z0
N5 G91 G00 X50 Y35 S500 MO3
N10 G43 Z-25 T01.01
N15 G01 G007 Z-12
N20 G00 Z12
N25 X40
N30 G01 Z-17
N35 G00 G44 Z42 M05
N40 G90 X0 Y0
N45 M30
%프로그래밍 섹션 형식
단어 배열 규칙, 프로그램 세그먼트의 문자와 데이터를 블록 형식이라고 합니다.. 고정된 시퀀스 형식 및 구분 기호 (HT 또는 TAB) 블록 형식은 CNC 기록에 사용되었습니다.. 이 두 가지 프로그램 세그먼트 형식이 통과되면, the word address variable program segment format is widely used at home and abroad, also known as the word address format.
In this format, the program word length is not fixed, and the number of program words is also variable. Most CNC systems allow the sequence of program words to be arranged arbitrarily, so they belong to the variable block format. 하지만, in most cases, for the convenience of writing, inputting, checking and proofreading, program words are arranged in a certain order in the program segment.
The programming instructions of CNC machine tools use detailed formats to classify and specify the details of programming: The characters used in programming, the sequence and word length of the program words in the program segment, 등. 예::/ NO3 G02 X+053 Y+053 I0 J+053 F031 S04 T04 M03 LF
The detailed format classification description of the above example is as follows: N03 is the sequence number of the program segment; G02 means that the processing track is a clockwise arc; X+053, Y+053 indicate the coordinates of the end point of the arc to be processed; I0, J+053 represent the center coordinates of the arc to be processed; F031 is the processing feed rate; S04 is the spindle speed; T04 is the tool number of the tool used; M03 is an auxiliary function command; LF block end instruction; /Select instructions for skipping. The function of skip selection instruction is: On the premise that the program remains unchanged, the operator can choose whether to execute or not to execute the blocks in the program with skip selection instructions. The method of selection is usually by turning the step selection switch on the operation panel to ON or OFF to realize that the program segment with “/” is not executed or executed.

milwaukee wisconsin machining services

정밀 조립 기계 부품 클램핑

Programming of CNC machining steel parts

CNC machining parts different program structure
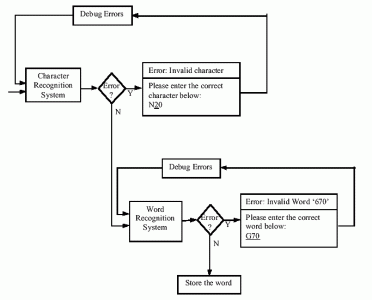
CNC machining components Program execution process
Execution of the program
This is sometimes encountered in the preparation of processing programs: A group of blocks appears multiple times in a program, or it is used in several programs. We can extract this group of program segments, name them and store them separately. This group of program segments is a subroutine. A subroutine is a section of processing program that can be called by appropriate machine control instructions, and it generally has an independent meaning in processing. 첫 번째 레벨의 서브루틴을 호출하는 명령이 있는 처리 프로그램을 메인 프로그램이라고 합니다.. 서브루틴의 명령도 프로그램 세그먼트입니다., 일반적으로 서브루틴 호출 명령으로 구성됩니다., 서브루틴 이름, 그리고 통화 횟수. 구체적인 규칙과 형식은 시스템마다 다릅니다.. 예를 들어, 그것은 또한 "서브루틴 호출 아니요. 55 한 번", FANUC 시스템은 "M98 P55.", 미국 A-B 회사 시스템을 사용합니다. "P55x".
서브루틴은 중첩될 수 있습니다., 그건, 층별로. 상위 레벨과 다음 레벨의 관계는 메인 프로그램과 첫 번째 레벨 서브루틴의 관계와 동일합니다.. 설정할 수 있는 최대 레이어 수는 특정 CNC 시스템에 따라 다릅니다.. The form and composition of the subroutine are roughly the same as the main program: The first line is the subroutine number (name), the last line is the "subroutine end" instruction, and the main body of the subroutine is between them. 하지만, the function of the main program end instruction is to end the main program and reset the CNC system. The instructions have been standardized, and each system uses M02 or M30; The function of the subroutine end instruction is to end the subroutine, return to the main program or the upper level subroutine. The commands are not unified in various systems, such as M99 for FANUC system, M17 for Siemens system, and M02 for system of American A-B company.
User macros (programs) can be used in CNC machining programs. The so-called macro program is a subroutine containing variables. 프로그램 내에서 매크로 프로그램을 호출하는 명령어를 사용자 매크로 명령어라고 합니다., 시스템이 사용자 매크로 프로그램을 사용할 수 있는 기능을 사용자 매크로 기능이라고 합니다.. 실행시, 사용자 매크로 기능을 실행하려면 사용자 매크로 명령만 작성하면 됩니다..
사용자 매크로의 가장 큰 특징은:
● 사용자 매크로에서 변수를 사용할 수 있습니다.;
●계산식 사용 가능, 터닝 스테이트먼트 및 다양한 기능
●사용자 매크로 명령을 사용하여 변수에 값을 할당할 수 있습니다..
CNC 공작 기계는 그룹 기술을 사용하여 부품을 가공합니다., 배치 크기를 확장할 수 있는, 프로그래밍을 줄이다, 경제적 이익을 향상시키고. 그룹처리에서는, 부품이 분류되어 있어요, 이러한 유형의 부품에 대해 처리 프로그램이 컴파일됩니다., instead of editing a program for each part. When processing the same type of parts with different sizes, the main convenience of using user macros is that variables can be used instead of specific values. When it comes to actual processing, it is only necessary to assign the actual size value of this part to a variable with a user macro command.
문의하기
이메일을 기다리는 중, 이내에 답변해 드리겠습니다. 12 필요한 귀중한 정보를 몇 시간 동안.
 English
English العربية
العربية 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Slovenčina
Slovenčina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Türkçe
Türkçe





