Le perçage est une découpe CNC semi-fermée. La température de coupe est très élevée lors du processus de perçage de l'alliage de titane, le rebond après le forage est important, les copeaux de forage sont longs et fins, facile à coller et pas facile à décharger. Le perçage du titane provoque souvent une morsure du foret, tordu, et ainsi de suite. Donc, le foret doit avoir une résistance élevée et une bonne rigidité, et l'affinité chimique entre le foret et l'alliage de titane est faible. Il est préférable d'utiliser des forets en carbure cémenté, mais le plus couramment utilisé à l'heure actuelle reste les forets hélicoïdaux, après avoir pris quelques mesures pour améliorer, de meilleurs résultats peuvent également être obtenus.
(1) Améliorer les forets: Afin de répondre aux besoins des forets CNC en alliage de titane, the following improvement measures should be taken for twist drills:
Increase the top angle of the drill bit, 2Ф=135°~140°; Increase the clearance angle at the outer edge of the drill bit, taking 12°~15°; Increase the helix angle, p=35°~40°; Increase the thickness of the drill bit core and take (0.22~0.4) do (do is the diameter of the drill bit).
Use “S” shape or “X” shape to sharpen the chisel edge of the drill, the chisel edge length b=(0.08~0.1)do, while ensuring that the symmetry of the chisel edge is ≤0.06 mm. Both types of chisel edges can form a second cutting edge, which plays a role of chip separation and reduces the axial force during drilling.
The most commonly used is to grind a cutting edge shape suitable for drilling titanium alloys on a twist drill. C'est, the titanium alloy group drill, the shape of the cutting part is shown in Figure 7-1. In the figure, the outer and inner cutting edge angles 2φ and 2φ′ are 130°~140° when the drill diameter do>3~10mm, and 125°~140° when do>10~30 mm;
The clearance angle α of the outer edge is 12°~18° when do>3~10 mm, and 10°~15° when do>10~30 mm;
Chisel edge angle ψ=45°;
Internal cutting edge angle γτ=-10°~-15°;
Inner blade angle τ=10°~15°;
The relief angle of the arc blade aR=18°~20°.
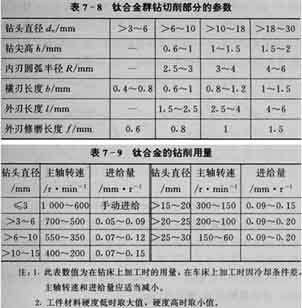
Relevant parameters and drilling amount of titanium alloy group drill
See Table 7-8 and Table 7-9 for the relevant parameters and drilling quantities of titanium alloy group drills.
Four guiding blades are made on the drill bit to increase the section moment of inertia of the drill bit, improve rigidity, and naturally form two auxiliary cooling grooves. The durability is about 3 times higher than that of standard drills, and the cutting temperature is reduced by about 20%. En même temps, the amount of hole expansion is reduced due to the stable guiding. Par exemple, the hole expansion of a Ф3 mm four-flute drill bit is 0.03~0.04 mm, while the standard drill bit is 0.05~0.06 mm.
(2) Choose a suitable gun drill: When drilling deep holes with a titanium alloy aspect ratio greater than 5, when the hole diameter is less than or equal to 30 mm, a cemented carbide gun drill is generally used, comme le montre la figure 7-2; When the hole diameter is greater than 30 mm, a cemented carbide BTA drill bit or jet suction drill is used. Use the gun drill shown in Figure 7-2 to drill the hole of TC4, the hole depth is 204 mm (length-to-diameter ratio is about 26), and the surface roughness Ra is 1.6 µm. The productivity is increased by 4 fois, the chips are in the shape of “Plum” ou “C”, and chip removal is normal.
Water-based cutting fluids should not be used when drilling deep holes, because water may form steam bubbles on the cutting edge at high temperatures, which may easily generate built-up edges and make drilling unstable. It is advisable to use N32 engine oil and kerosene, the ratio of which is 3:1 ou 3:2, and sulfurized cutting oil can also be used.
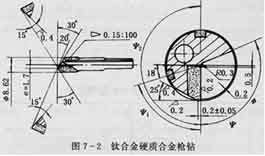
Cemented carbide gun drills for drilling titanium alloys
Lorsque vous utilisez un pistolet au carbure pour percer des trous profonds avec un rapport longueur/diamètre supérieur à 30. Forage vibrant en appliquant une vibration inférieure à 100 Hz dans la direction axiale peut rendre la rugosité de surface Ra de la pièce 0.3 μm et augmenter la productivité de 5 fois. Les paramètres spécifiques sont Vc=17 m/min, f=0,033 min/r, l'amplitude est 0.07 mm, la fréquence est 35 Hz, la rondeur de la pièce est 4 µm, and the surface roughness Ra is 0.33 µm.
(3) Choisissez le bon liquide de coupe: Un liquide de coupe électrolytique peut être utilisé lors du perçage de trous peu profonds. Ses ingrédients sont l'acide sébacique 7%-10%, triéthanolamine 7%-10%, glycérol 7%-10%, acide borique 7%-10%, nitrite de sodium 3%-5%, et le reste c'est de l'eau.
 English
English العربية
العربية 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Slovenčina
Slovenčina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Türkçe
Türkçe

