Silmänräpäyksessä, Olen käyttänyt CNC-sorveja yli kymmenen vuotta, ja heillä on jonkin verran koneistustaitoja ja kokemusta CNC-sorveista. Sisältää eri materiaalien sorvauksen (ruostumaton teräs, alumiini, kuparihiiliterästä, titaani, sementoitu kovametalli, jne.). Käsiteltyjen osien toistuvan vaihdon ja rajoitettujen tehdasolosuhteiden vuoksi, kymmenen vuoden ajan olemme ohjelmoineet itseämme, työkalujen asettaminen itse, virheenkorjaus ja osien viimeistely itse. Yhteenvetona, käyttötaidot on jaettu seuraaviin kohtiin.

Operating CNC lathe
One, Programming skills of lathe
Because our factory has high requirements for the accuracy of processed products, the things that need to be considered when programming are:
1. Processing sequence of parts:
Drill first, then turn the flat end (this is to prevent shrinkage during drilling);
Rough turning first, then fine turning (this is to ensure the accuracy of parts);
The position with large tolerance is processed first, and the final processing with small tolerance (this is to ensure that the surface of small tolerance size is not scratched and prevent deformation of parts).
2. Choose reasonable speed, feed and depth of cut according to material hardness:
1) Select carbon steel material with high speed, high feed rate and large cutting depth. Kuten: 1Gr11, select S1600, F0.2, and cut depth 2mm;
2) Low speed, low feed rate and small cutting depth are selected for hard alloy. Kuten: GH4033, select S800, F0.08, and cut depth 0.5mm;
3) Choose low speed, high feed rate and small cutting depth for titanium alloy. Kuten: Ti6, select S400, F0.2, and cut depth 0.3mm.
Take the processing of a certain part as an example: the material is K414, which is a very hard material. After many tests, the final selection is S360, F0.1, and the depth of cut 0.2, in order to process qualified parts.

CNC-sorviporausprosessi
two, Tool setting skills of lathe
Tool setting is divided into: tool setting with tool setting instrument and direct tool setting. The tool setting technique mentioned below is direct tool setting.
First select the center of the right end face of the part as the tool setting point and set it as the zero point. After the machine tool returns to the origin, jokainen käytettävä työkalu on asetettu nollapisteeksi kappaleen oikean päätypinnan keskipisteeseen;
Kun työkalu koskettaa oikeaa päätypintaa, syötä Z0 ja mittaa napsauttamalla, ja mitattu arvo tallennetaan automaattisesti työkalun korjausarvoon, mikä tarkoittaa, että Z-akselin työkalu on asetettu. X-työkaluasetus on leikkaustyökalun koeasetus, ja osan ulkokehä käännetään työkalulla. Mittaa käännetyn ulkoympyrän arvo (esimerkiksi, x on 20 mm) ja kirjoita x20, napsauta Mittaa, työkalun kompensointiarvo tallentaa automaattisesti mitatun arvon, ja sitten x-akseli suorittaa myös työkalun asetuksen;
Tämä työkalun asetustapa ei muuta työkalun asetusarvoa edes koneen sammuttamisen jälkeen. Se soveltuu saman osan massatuotantoon pitkään, jonka aikana sorvin ei tarvitse kalibroida työkalua uudelleen uudelleenkäynnistyksen jälkeen.

Yleiset työkalun asetuslaitteet CNC-sorveille
kolme, Sorvin virheenkorjaustaidot
Kun osat on ohjelmoitu, koeleikkaus ja virheenkorjaus vaaditaan työkalun säätämisen jälkeen. Jotta ohjelman virheet ja työkaluasetusvirheet eivät aiheuta törmäysonnettomuuksia, meidän pitäisi ensin suorittaa tyhjäkäyntisimulaatiokäsittely. Työstökoneen koordinaattijärjestelmässä, siirrä työkalua oikealle 2-3 kertaa osan kokonaispituus; Aloita sitten simuloinnin käsittely. Simulaatiokäsittelyn jälkeen, varmista, että ohjelma ja työkaluasetukset ovat oikein, ja aloita sitten osien käsittely. Ensimmäisten työstöosien valmistumisen jälkeen, ensimmäinen itsetestaus, kelpoisuuden vahvistamiseksi, tarkista löytääksesi kokopäiväisiä tarkastajia, pätevät päätoimiset tarkastajat vahvistivat tämän osoittavan käyttöönoton päättymisen.

CNC-sorvin koeleikkaus ja virheenkorjaus
neljä, Viimeistele osien koneistus
Kun ensimmäisen prototyypin koeleikkaus on valmis, osat valmistetaan massatuotantona. kuitenkin, prototyypin hyväksytty tuote ei tarkoita, että koko osaerä hyväksytään, koska käsittelyprosessissa, työkalu kuluu käsittelymateriaalien erojen vuoksi. Kun käsittelymateriaali on pehmeää, työkalun kuluminen on pientä, ja työstömateriaali on kovaa ja työkalu kuluu nopeasti. Siksi, käsittelyssä, on tarpeen tarkistaa lisää, lisää ja vähennä työkalun kompensointiarvoa ajoissa varmistaaksesi, että osat ovat kelvollisia.
Ota osa esimerkkinä, käsittelymateriaali on K414, ja käsittelyn kokonaispituus on 180 mm. Erittäin kovan materiaalin ansiosta, työkalu kuluu erittäin nopeasti käsittelyn aikana. Aloituspisteestä loppupisteeseen, muodostuu 10-20 mm kulma työkalun kulumisen vuoksi. Siksi, meidän on keinotekoisesti lisättävä ohjelmaan kompensaatioarvo 10-20 mm, jotta varmistetaan pätevät osat.
Sorvin käsittelyn perusperiaatteet: Karkea koneistus ensin, poista ylimääräinen materiaali työkappaleesta, ja lopeta koneistus; Vältä tärinää käsittelyn aikana; Vältä työkappaleen lämpödenaturoitumista käsittelyn aikana. Liiallisen kuormituksen aiheuttamaan tärinään on monia syitä; It may be the resonance of the machine tool and the workpiece, or the rigidity of the machine tool may be insufficient, or it may be caused by the passivation of the tool. We can reduce vibration by the following methods; Reduce the transverse feed and processing depth, check whether the workpiece is clamped securely, increase the speed of the tool and reduce the speed to reduce the resonance. Lisäksi, check whether it is necessary to replace a new tool.
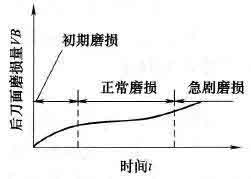
Turning tool wear process and blunt standard
Fives, The experience of preventing machine collision
Machine tool collision is a great damage to the accuracy of the machine tool, and it has different effects on different types of machine tools. Yleisesti ottaen, it has a greater impact on machine tools with low rigidity. Siksi, for high-precision CNC lathes, collisions must be absolutely eliminated. As long as the operator is careful and masters certain anti-collision methods, collisions can be prevented and avoided.
The main reason for the collision:
1> Enter the diameter and length of the tool incorrectly;
2> The size of the workpiece and other related geometric dimensions are entered incorrectly, and the initial position of the workpiece is incorrectly positioned;
3> The workpiece coordinate system of the machine tool is set incorrectly, or the zero point of the machine tool is reset during the machining process, which causes a change. Most of the machine tool collisions occur during the rapid movement of the machine tool. The collisions that occur at this time are also the most harmful and should be absolutely avoided. Siksi, the operator must pay special attention to the machine tool in the initial stage of executing the program and when the machine tool is changing tools. Tällä hetkellä, once the program is edited incorrectly and the diameter and length of the tool are entered incorrectly, collisions are likely to occur. At the end of the program, if the NC axis retracts the tool in a wrong sequence, then collisions may also occur.
In order to avoid the collision mentioned above, the operator must give full play to the sensory functions when operating the machine tool. Observe whether there is abnormal movement of the machine tool, whether there is spark, whether there is noise and abnormal noise, whether there is vibration, whether there is a burning smell. Ohjelma tulee lopettaa välittömästi, kun epänormaali tilanne havaitaan, ja työstökone voi jatkaa toimintaansa sen jälkeen, kun valmiustilan ongelma on ratkaistu.
 English
English العربية
العربية 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Slovenčina
Slovenčina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Türkçe
Türkçe

