Legen Sie die geometrischen Parameter von Dreh- und Fräswerkzeugen aus Titan fest, um die Produktqualität von Teilen aus Titanlegierungen zu verbessern. Die Produkte werden schnell und pünktlich geliefert.
(1) Der Spanwinkel des Werkzeugs γ0: Die Kontaktlänge zwischen Titanlegierungsspänen und der Spanfläche ist kurz. Wenn der Spanwinkel klein ist, die Kontaktfläche des Chips kann vergrößert werden, damit sich die Schneidwärme und die Schneidkraft nicht übermäßig in der Nähe der Schneidkante konzentrieren. Verbessern Sie die Wärmeableitungsbedingungen, und kann die Schneidkante stärken und die Möglichkeit von Absplitterungen verringern. Das Drehen von Titan erfordert im Allgemeinen γ0=5°~15°.
(2) The clearance angle α0 of the tool: The processed surface of titanium alloy has large elastic recovery and serious cold hardening. The use of a large relief angle can reduce the friction, adhesion, adhesion, tearing and other phenomena caused to the flank surface, so as to reduce the wear of the flank surface. The relief angle of various cutting titanium alloy tools is basically greater than or equal to 15°.
(3) The leading deflection angle κr and the secondary deflection angle κ´r of the milling tool: Beim Fräsen von Titanlegierungen, the cutting temperature is high and the elastic deformation tends to be large. When the rigidity of the process system allows, the entering angle should be reduced as much as possible to increase the heat dissipation area of the cutting part and reduce the load per unit length of the cutting edge. Allgemein, κr=30° is used, and κr=45° for rough machining. Reducing the secondary deflection angle can strengthen the tool tip, which is beneficial to heat dissipation and reduces the surface roughness value of the machined surface. Generally take κ´r =10°~15°.
(4) The blade inclination angle of the tool λs: Due to the rough surface and uneven surface structure of the blank, the cutting edge is prone to chipping during rough turning. In order to increase the strength and sharpness of the cutting edge, the sliding speed of the chip should be increased. Allgemein, λs = -3°~-5° is used for rough turning, and λs = O° for fine turning.
(5) The radius of the nose arc of the tool rε: Beim Drehen von Titanlegierungen, the tool tip is the weakest part, which is easy to chip and wear, so it needs to grind the tool tip arc. Generally rε=0.5~1.5mm.
Negative chamfering (bγ=0.03~0.05 mm, γ01=-10°~0°) is used during turning, and the arc radius of the bottom of the chip flute is Rn=6~8 mm.
Zusätzlich, the quality of tool sharpening is also very important to improve its durability. Carbide cutting tools should be sharpened with diamond grinding wheels. The cutting edge must be sharp when cutting, the surface roughness Ra value of the front and rear cutting faces should be less than 0.4um, and the cutting edge is not allowed to have tiny gaps. After the tool is sharpened and ground, its durability can be increased by 30%.
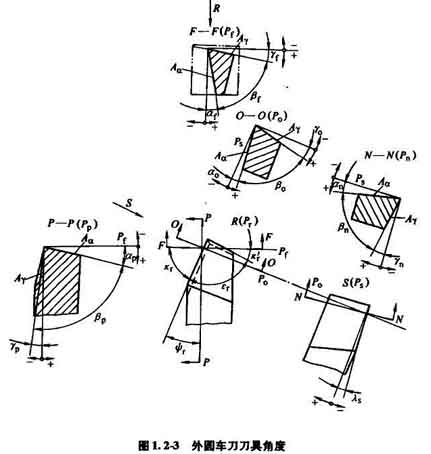
Design of cutting edge angle for turning and milling titanium
 English
English العربية
العربية 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Slovenčina
Slovenčina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Türkçe
Türkçe

