External turning as an example, there are three turning components: main turning force Fc (Fz), depth resistance Fp (Fy) (also called radial force), feed resistance Ff (Fx) (also called axial force).
The main turning force is the most important. In the case of neglecting the power consumption of Ff, the turning power is Pc=Fc.v×103 (kw) where Fc and the unit N; the unit of v is m/min.
In the early years, the cutting force test during high-speed turning was carried out. As shown in Figure 1, when turning 45 steel (normalizing, HB187), when the turning speed is increased from 100m/min to 270m/min, the main turning force is reduced by about 7%. As shown in Figure 2, when turning cast aluminum alloy ZL10 (HB45), when the turning speed is increased from 100m/min to 720m/min, the main turning force is reduced by about 50%.
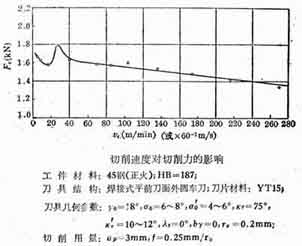
When turning steel, the effect of cutting speed on turning force
Figure 1. The effect of turning speed on cutting force when turning 45 steel (ap=3mmf=0.25mm/r)
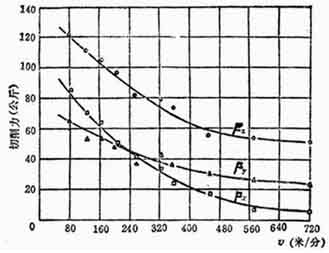
When turning ZL10, the influence of cutting speed on turning force
Figure 2. The effect of turning speed on cutting force when turning ZL10 (ap=4mmf=0.3mm/r)
A university used LT55 ceramic turning tool to turn 45 steel (quenched and tempered, HRC35~40). The relationship between turning force and cutting speed is shown in Figure 9. It can be seen from Figure 9 that the cutting force is the largest when the turning speed is about 300m/min, and it decreases immediately. The cutting force does not change much when the turning speed is above 500m/min.
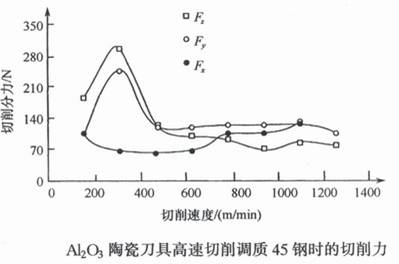
Cutting force of ceramic tools when turning quenched and tempered steel
Figure 3, the cutting force when turning 45 quenched and tempered steel with ceramic turning tool
A certain university conducted a turning force test of quenched and tempered steel (HRC30~32) and hardened steel (HRC50~52). Quenched and tempered steel: ap=0.2~0.5mm, f=0.1~0.25mm/r, v=700~1000m/min. Hardened steel: ap=0.15~0.5mm, f=0.1~0.25mm/r, v=100~400m/min. A three-factor formula for the three-way turning force is established (Table 1).
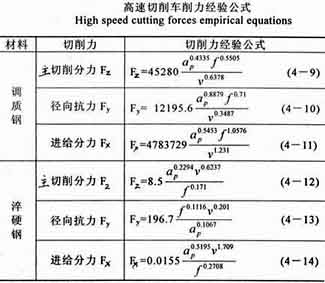
Three-factor formula of high-speed turning force
Table 1. Three-factor formula of high-speed turning force
The turning rate manual lists: the cutting force experience of turning medium carbon structural steel at normal speed, the formula is
Fz=Czap1f 0.75v-0.15
Fy=Cyap0.90f 0.60v -0.3
Fx=Cxap1f 0.5v-0.4
Compared with Table 1, there is a big difference. The formula in Table 1 may be problematic. Compared with turning, the milling force formula is more complicated, because in addition to the three elements of cutting consumption, there are also factors such as the number of teeth of the milling cutter, the diameter of the milling cutter, and the milling width. The multi-factor empirical formula of cutting force and turning power established in the past for end milling at general cutting speed. The turning force formula under modern high-speed turning is not yet known.
A certain university filled this vacancy. A three-factor formula for turning force is made:
Within the range of ap=0.5~1mm, f=0.05~0.2mm/r, v=251~1256m/min,
Fc=5018ap0.344fz0.364v-0.394 (turning 45 steel)
Fc=864ap0.384fz0.176v-0.287 (turned aluminum alloy 5A02)
It seems that the data obtained from the experiment is not ideal, which can be used for reference.
A certain university used ceramic cutters to turn hardened steel, high-strength steel, and hard nickel cast iron at high speed and did a fruitful turning force test.
(1) LT55 (Al2O3TiC) ceramic tool for turning hardened 45 steel (HRC50~55), v =30~120m/min, ap=0.35~1.4mm, f=0.08~0.32mm/r, Fz=2525 ap0.99 f 0.80 v-0.01(N)
(2) LT55 tool is used for turning ultra-high-strength steel 35CrMnSiA (HRC45~48), the cutting amount range is the same as above.
Fz=2779 ap0.79 f 0.59 v -0.08(N)
(3) SG-4 (Al2O3-TiC, WC) Ceramic Tool cutting hardened high carbon tool steel (HRC55 ~ 62), the cutting amount in the range above.
Fz=3444 ap0.88 f 0.65 v -0.12(N)
(4) SG-4 tool is used for turning hardened 45 steel (HRC50~55), the cutting amount range is the same as above.
Fz=2309 ap1.04 f 0.75 v -0.01(N)
(5) AT6 (Al2O3―TiC) ceramic tool for turning hard nickel cast iron (HRC56~62)
V =50~70m/min, ap=1.5~2.3mm, f=0.09~0.16mm/r
Fz=1210 ap0.73f 0.42v-0.09(N)
The cutting force test data for high-speed turning of hard materials with ceramic tools is more credible.
 English
English العربية
العربية 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Slovenčina
Slovenčina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Türkçe
Türkçe

